Shinkansen Tickets – Buy Bullet Train Tickets
Single Shinkansen tickets may be the way to go for your trip to Japan
With the 70% price increase of the nationwide Japan Rail Pass, it may be worth considering if single train tickets or regional passes are the right fit for your trip. Whether you’re eager for high-speed escapades on the Shinkansen, serene views aboard scenic railways through the countryside, or engaging in a deep dive into historical locales, you can now get individual train tickets which cover the comprehensive rail system in Japan.

Why you should reserve your train tickets before your trip to Japan:
- Ease of Booking: Booking your tickets online is significantly simpler than navigating on the ground purchases, particularly in Japan. This approach ensures a seamless experience, free from the complexities of using ticket machines or standing in lines at busy stations.
- Secured Seating: Opting for booking before you go guarantees you a seat, especially crucial during peak travel periods. This is a game-changer during Japan’s busy tourist seasons, such as the cherry blossom (sakura) and autumn foliage (momiji) seasons, and the bustling New Year’s holidays.
- Planned Itinerary and Budget: By securing your tickets online, It allows you to get organised and understand the travel costs ahead of your journey.
About The Japan Bullet Trains
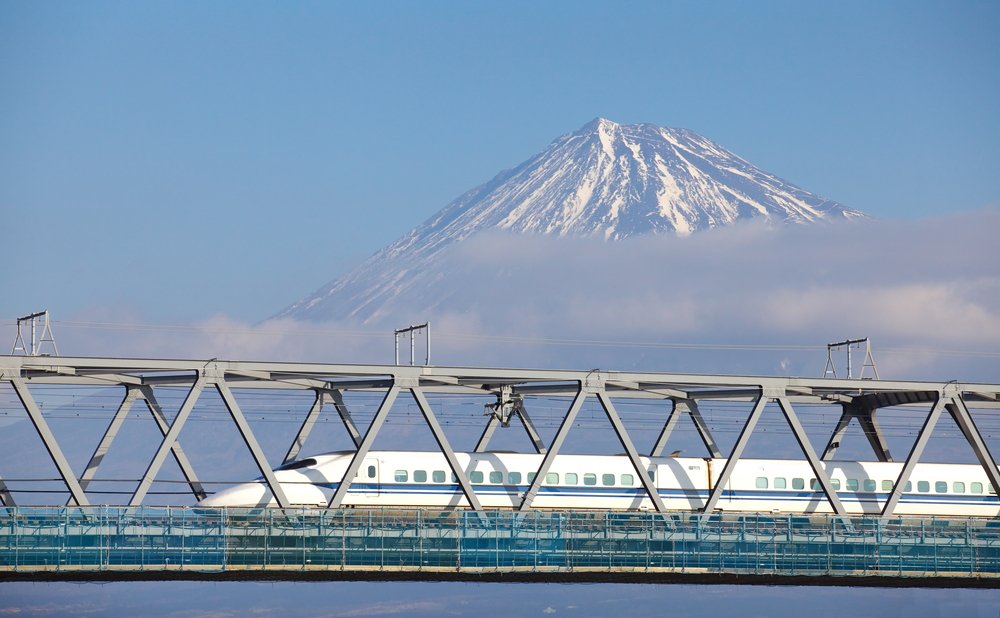
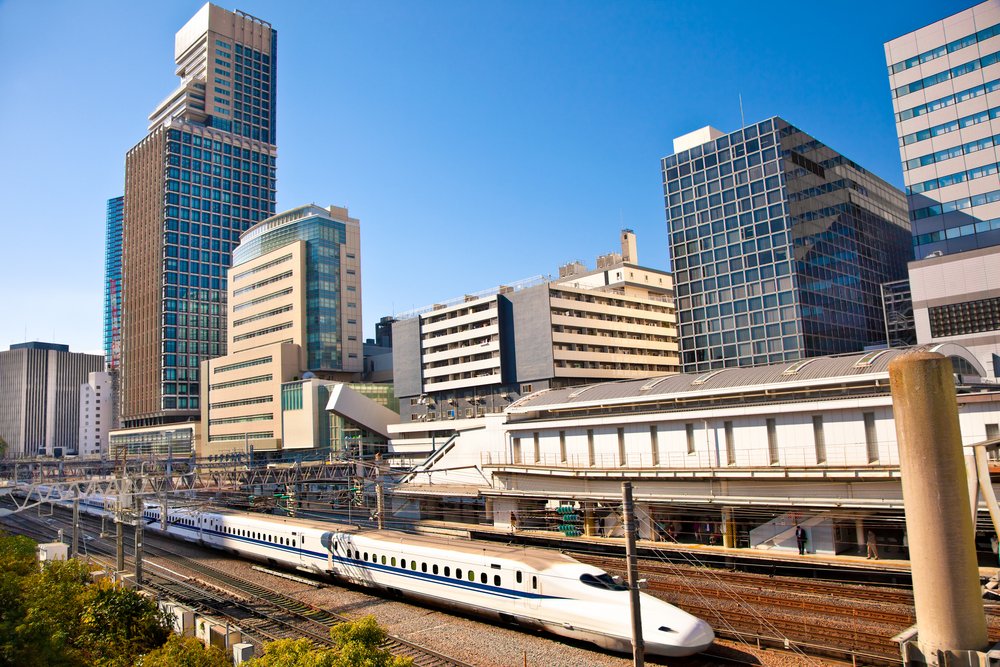
Japan’s major cities are connected by a network of high speed trains known as Shinkansen. The network operated by Japan Railways (JR) has been progressively developed on the main islands of Honshu, Kyushu and Hokkaido since the 1960s. It provides a stark example of cutting edge Japanese technology, connecting the bustling capital city of Tokyo with cities extending as far as Aomori in the north and Kagoshima in the south.
trains currently transport a staggering 150 million passengers per year. Riding on one is an essential part of the tourist experience when visiting Japan. These trains can travel up to 320 kilometres per hour. To put that speed into perspective, if we had Shinkansen trains in Australia they’d be able to travel between Sydney and Melbourne in under three hours!
Incredibly, for most of their journey, Shinkansen trains don’t make contact with the track. Instead, they hover 10 centimetres above the track as they are propelled through the air by electrically-charged magnets on either side of the line.
Besides their incredible speed, they have a great reputation for:
- consistently departing and arriving on time;
- comfort (there’s plenty of room with their reversible seating arrangements);
- quiet and efficient operation;
- cleanliness;
- safety (they have one of the best safety records in the world!)
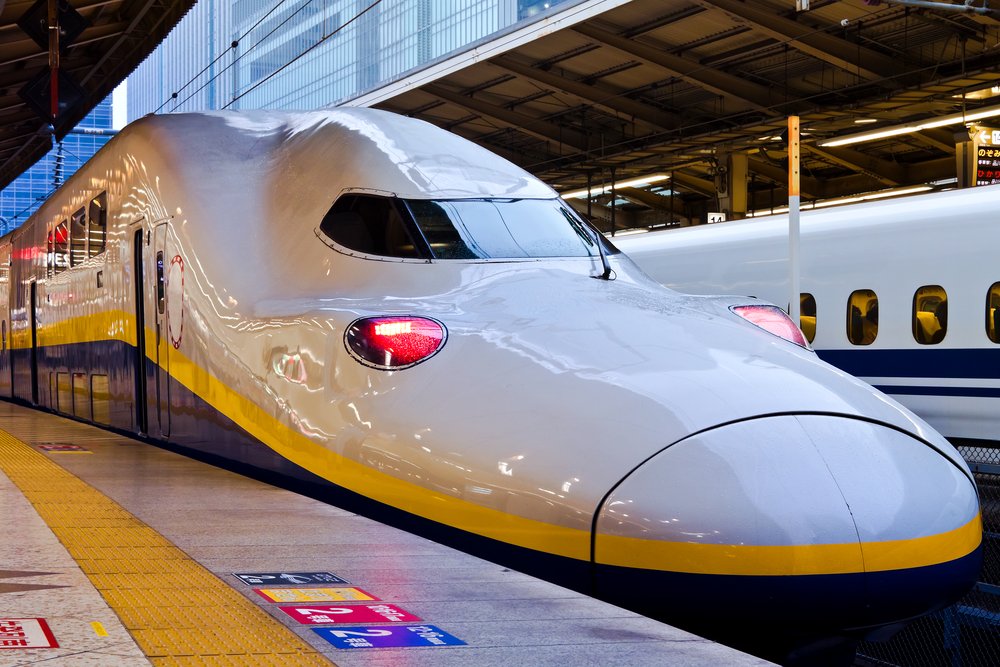

Shinkansen in Japan
Popular Shinkansen Ticket Routes
| Popular Routes | Detailed Transport Itinerary Including Time/Single Price |
| Narita Airport to Tokyo | Narita Express: 63 minutes |
| Shinkansen Hikari: 173 minutes | |
| Tokyo to Kyoto | Shinkansen Hikari: 158 minutes |
| Tokyo to Kyoto (Nozomi) | Shinkansen Hikari: 123 minutes |
| Tokyo to Hiroshima | Shinkansen Hikari: 191 minutes Change over at Shin-Kobe station Shinkansen Sakura: 73 minutes |
| Tokyo to Hiroshima (Nozomi) | Shinkansen Nozomi: 173 minutes |
| Tokyo to Sapporo | Shinkansen Hayabusa: 254 minutes Change over at Shin-Hakodate-Hokuto station LTD. EXP Super Hokuto: 204 minutes t |
| Tokyo to Hakone (Odawara Station) | Shinkansen Kodama: 35 minutes |
| Tokyo to Hakone (Odawara Station) 2 | JR Tokaido Line Rapid: 74 minutes |
| Tokyo to Kawaguchiko | JR Chuo Special Rapid Service for Takao: 56 minutes Change over at Takao(Tokyo) station JR Chuo Line: 36 minutes Change over at Otsuki Station |
| Tokyo to Nagano | Shinkansen Hakutaka: 92 minutes |
| Tokyo to Nagano 2 | Shinkansen Kagayaki: 84 minutes |
| Tokyo to Nagano 3 | Shinkansen Asama: 104 minutes |
| Shinkansen Hikari: 104 minutes change over at Nagoya LTD. EXP Hida: 142 minutes total 15,010 yen |
|
| Kyoto to Hiroshima | Shinkansen Hikari: 28 minutes change over at Shin-Kobe Shinaksen Sakura: 74 minutes total 11,290 yen |
| Kyoto to Osaka | JR Special Rapid Service: 28 minutes |
| Kyoto to Nara | JR Nara line Rapid Service: 46 minutes |
| Kyoto to Takayama | Shinkansen Hikari: 36 minutes change over at Nagoya station LTD. EXP Hida: 142 minutes |
| Shin-Osaka to Hiroshima | Shinkansen Sakura: 88 minutes |
| Osaka to Nara | JR Yamatoji Rapid Service: 50 minutes |
| Osaka to Kyoto | JR Special Rapid Service: 29 minutes |
| Tokyo to Nagoya | Shinkansen Hikari: 125 minutes OR Shinkansen Kodama: 169 minutes |
| Nagoya to Kyoto | Shinkansen Hikari: 36 minutes OR Shinkansen Kodama: 48 minutes |
| Nagoya to Shin-Osaka | Shinkansen Hikari: 51 minutes OR Shinkansen Kodama: 64 minutes |
| Nagoya to Hiroshima | Shinkansen Hikari: 65 minutes Change over at Shin-Kobe Station Shinkansen Sakura: 73 minutes |
| Tokyo to Nikko | Shinkansen Yamabiko: 50 minutes Change over at Utsunomiya Station JR Niko Line for Nikko: 49 minutes |
| Kyoto to Himeji | Shinkansen Hikari: 54 minutes OR JR Special Rapid Service for HIMEJI: 28 minutes Arrive at Osaka, depart from same track Osaka JR Special Rapid Service for HIMEJI: 63 minutes |
| Osaka to Himeji | JR Special Rapid Service for HIMEJI: 64 minutes: OR JR Special Rapid Service for TSURUGA: 4 minutes Change at Shin-Osaka Station Shinkansen Kodama: 33 minutes |
| Himeji to Hiroshima | Shinkansen Hikari: 59 minutes OR Shinkansen Sakura: 59 minutes OR Shinkansen Kodama: 119 minutes |
| Kyoto to Fukuoka (Hakata Station): | Shinkansen Hikari: 28 minutes Change over at Shin-Kobe Station Shinkansen Sakura: 140 minutes |
| Hiroshima to Fukuoka (Hakata Station): | Shinkansen Hikari: 64 minutes OR Shinkansen Sakura: 65 minutes OR Shinkansen Kodama: 100 minutes |
| Nagano to Kyoto | Shinkansen Kagayaki: 66 minutes Change over at Kanazawa Station LTD. EXP Thunderbird: 133 minutes OR LTD. EXP (wide view) Shinano: 181 minutes Change over at Nagoya Station Shinkansen Hikari: 36 minutes |
| Kansai Airport to Kyoto | LTD. EXP train: 80 minutes: 3,370 yen |
| Kansai Airport to Osaka | JR Kansai Airport Rapid Service: 71 minutes |
| Odawara to Kyoto | Shinkansen Hikari: 123 minutes OR Shinkansen Kodama: 178 minutes |
The Network
The Shinkansen network has multiple rail lines:
- Tokaido (the most popular line that links Tokyo, Nagoya, Kyoto and Osaka: the stretch between Tokyo and Kyoto provides spectacular views of the iconic Mt Fuji)
- Sanyo (linking Osaka, Hiroshima and Fukuoka)
- Kyushu (linking Fukuoka and Kagoshima)
- Tohoku (linking Tokyo, Sendai, Morioka and Aomori)
- Joetsu (linking Tokyo and Niigata)
- Hokuriku (linking Tokyo and Kanazawa)
- Hokkaido (linking Aomori and Hakodate)
In addition, several additional lines are planned over the coming decades. One magnetic line between Tokyo and Nagoya that is scheduled for completion by 2027 will enable Shinkansen trains to travel at speeds up to 500 kilometres per hour.
A variety of Shinkansen train types operate on each existing line, ranging from express services that bypass various stations to those that stop at each station.

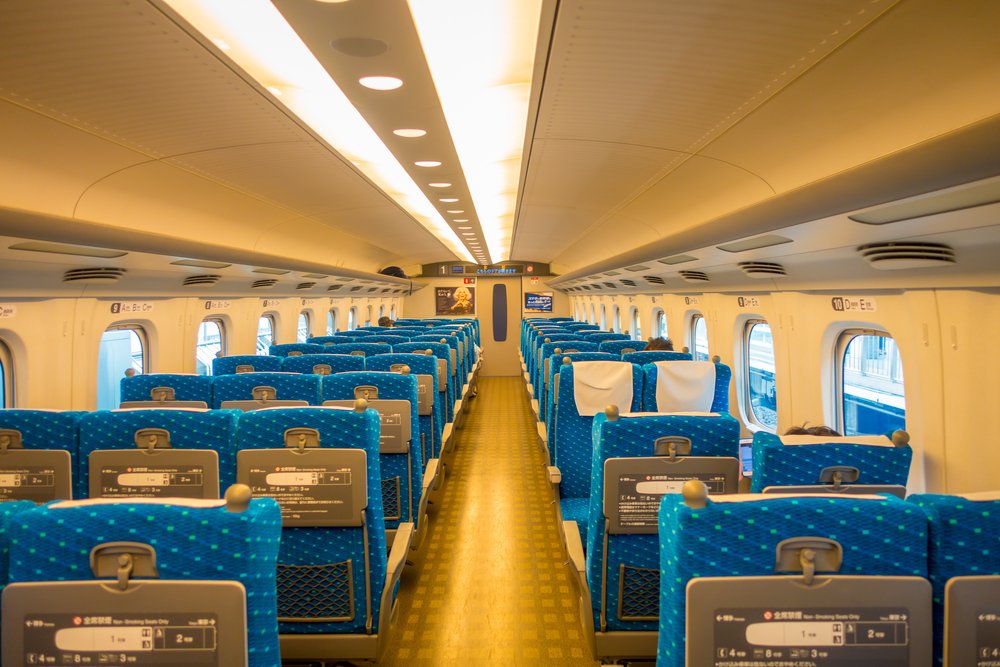
Seat Categories
Most Shinkansen trains offer two seat classes in separate cars, with some also offering a third class. These classes are:
1) Ordinary
These are regular seats and usually arranged in rows of 3×2. The size and foot space varies between Shinkansen trains, but they are generally comfortable. They provide considerably more foot space than economy seats on planes. Ordinary seats can also be reclined and they have foldout tables and pockets for magazines like on a plane, as well as open overhead shelves that can store small and medium-sized bags or suitcases.
There’s also usually enough space for two or three large suitcases behind the last row of seats in each Shinkansen Car. Each passenger is allowed to bring up to two pieces of luggage weighing less than 30 kilograms and not measuring more than 2 and a half metres combined in terms of height, width and depth.

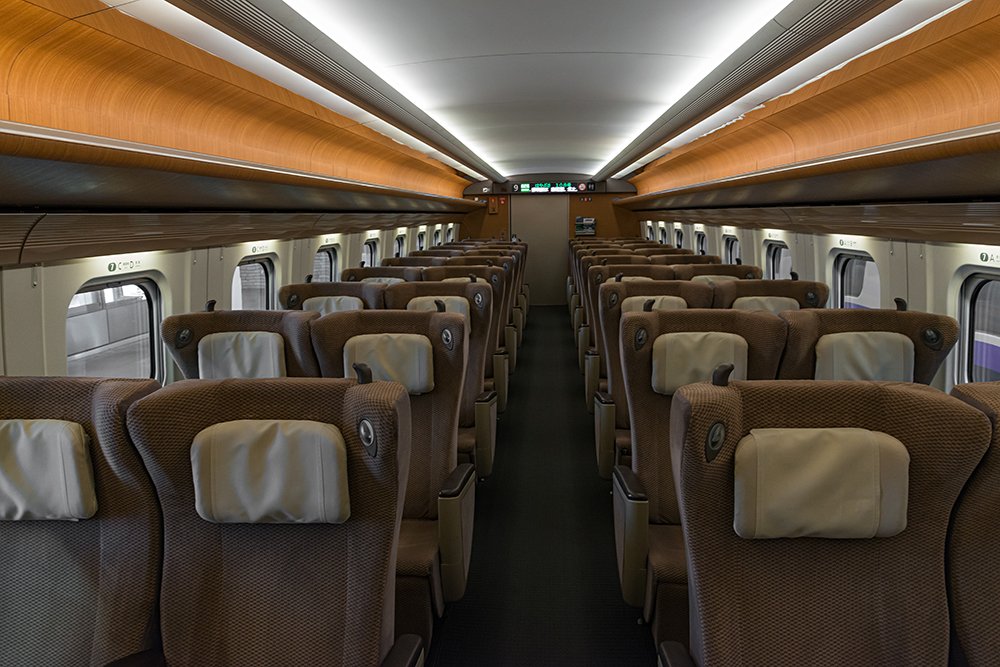
2) Green Car
Green Car is similar to business class on planes and is arranged in rows of 2×2. Seats are more spacious and comfortable than those in Ordinary class, and they have all of the other features of Ordinary Class. Depending on the type of Shinkansen service, they may also have a foot rest, reading light, radio, electrical outlet and a seat warmer. Green Cars are also less crowded than Ordinary Cars.

3) Gran
This is comparable to first class on planes. It’s available on the Tohoku, Hokuriku and Hokkaido Shinkansen trains. Gran class seats are the most spacious available, and passengers in them are entitled to additional amenities and services to those provided with both Green or Ordinary Cars.
Reserved and Non-Reserved Seating + How to make Seat Reservations
Most Shinkansen trains offer both reserved (shiteiseki) and non-reserved (jiyūseki) seating. However, a few services on the Tohoku, Hokkaido and Hokuriku Shinkansen lines only offer reserved seating. Bilingual signs on the Shinkansen trains and at station platforms indicate whether reserved and/or non-reserved seatings options are available.
All Green Car and Gran seats must be reserved in advance, along with any special needs seating (e.g. passengers with wheelchairs).
You can reserve a Shinkansen seat up to a month in advance via a JR ticket office. Doing this gives you the peace of mind that you’ll be able to travel in comfort when you want to. At peak travel times to popular destinations, seats can often be booked out several days in advance. To reserve seats, you need to provide:
- your departure and destination stations;
- the date of your travel;
- the time of your Shinkansen service;
- the seat class you require e.g. Ordinary, Green Car or Gran
You can also reserve a seat moments before your departure at a station ticket counter (midori no madoguchi), provided seats are still available. If you don’t speak Japanese, it’s recommended that you write your seat reservation details down on a piece of paper and hand it to the ticket officer to avoid confusion. Vending machines are also an option for Shinkansen seat reservations but you can order online befoer tou go.
Fares and Ticketing
a Shinkansen fare can be made up of several fees, but when you purchase online this fare will be combined and all included:
1) A base fare (jōshaken): This amount depends on how far you’re travelling. The greater the distance, the higher your base fare. You pay this amount whether you’re travelling on a Shinkansen train or an ordinary local train.
2) Shinkansen limited express supplement (tokkyūken): This is an additional charge for using a Shinkansen instead of a local train. Again, the greater the distance, the greater the fare.
3) Seat reservation fee: The seat reservation fee depends on whether it’s low season, regular season, or high season. It ranges from 320, 520 and 720 yen depending on the time of year. An additional supplement fee of 100-620 yen is applied for reserved seats on Nozomi, Mizuho, Hayabusa and Komachi trains. It’s usually combined with the express supplement into single ticket.
3) Green car fee: This is an additional fee you’ll pay for Green Car or Gran seating.

Boarding Shinkansen Trains
Regular Shinkansen ticket holders must queue and pass through automatic gates. Signs and announcements on Japanese platforms are bilingual (Japanese and English). You then will make your way to the Shinkansen platforms to board one of these trains. They are often in a separate part of the station or on a different level, but they may also be parallel to the regular train lines.
Virtually all Japanese stations have escalators or elevators if required. There is easy Shinkansen platform and train access for passengers in wheelchairs and mothers with strollers.
Displays on each Shinkansen platform will indicate upcoming Shinkansen arrivals and routes. Other signs painted on the platform indicate car door locations, numbers and seat classes (i.e. Ordinary, Green Car or Gran). It’s customary in Japan to line up in an orderly queue to board trains, especially for non-reserved seats. Reserved Shinkansen seats are numbered and lettered similarly to airline seats.
Riding on Shinkansen Trains
Just like on public transport in Australia, there are manners you should observe when riding Shinkansen trains in Japan:
- keep your voice down when you’re having a conversation;
- turn your phone to silent mode;
- have consideration for the person behind you when reclining your seat;
- don’t block aisles with your luggage.
Small food carts with a variety of snacks, drinks and boxed meals (bento) pass along the aisles at regular intervals on most Shinkansen trains. Some also have drink vending machines. Wi-Fi is available on the newest Shinkansen trains between Tokyo and Shin-Osaka and will progressively become available on others. However, you need to buy a subscription or a 1-day pass before you board the train to be able to access this Wi-Fi.
Multiple toilet and wash room facilities are available on all Shinkansen trains, with some being gender-specific. Most toilets are Western style and many modern Shinkansen trains also have disabled toilet facilities.
Smoking is not allowed on most Shinkansen trains, although a few older models allow smoking in small designated areas.